Previous
Deploy model
Inference is the process of generating output from a machine learning (ML) model.
You can run inference locally on a Viam machine, or remotely in the Viam cloud.
When you have deployed an ML model on your machine, you can run inference on your machine directly with the ML model service or using a vision service that interprets the inferences.
Entry-level devices such as the Raspberry Pi 4 can run small ML models, such as TensorFlow Lite (TFLite). More powerful hardware, including the Jetson Xavier or Raspberry Pi 5 with an AI HAT+, can process larger models, including TensorFlow and ONNX. If your hardware does not support the model you want to run, see Cloud inference.
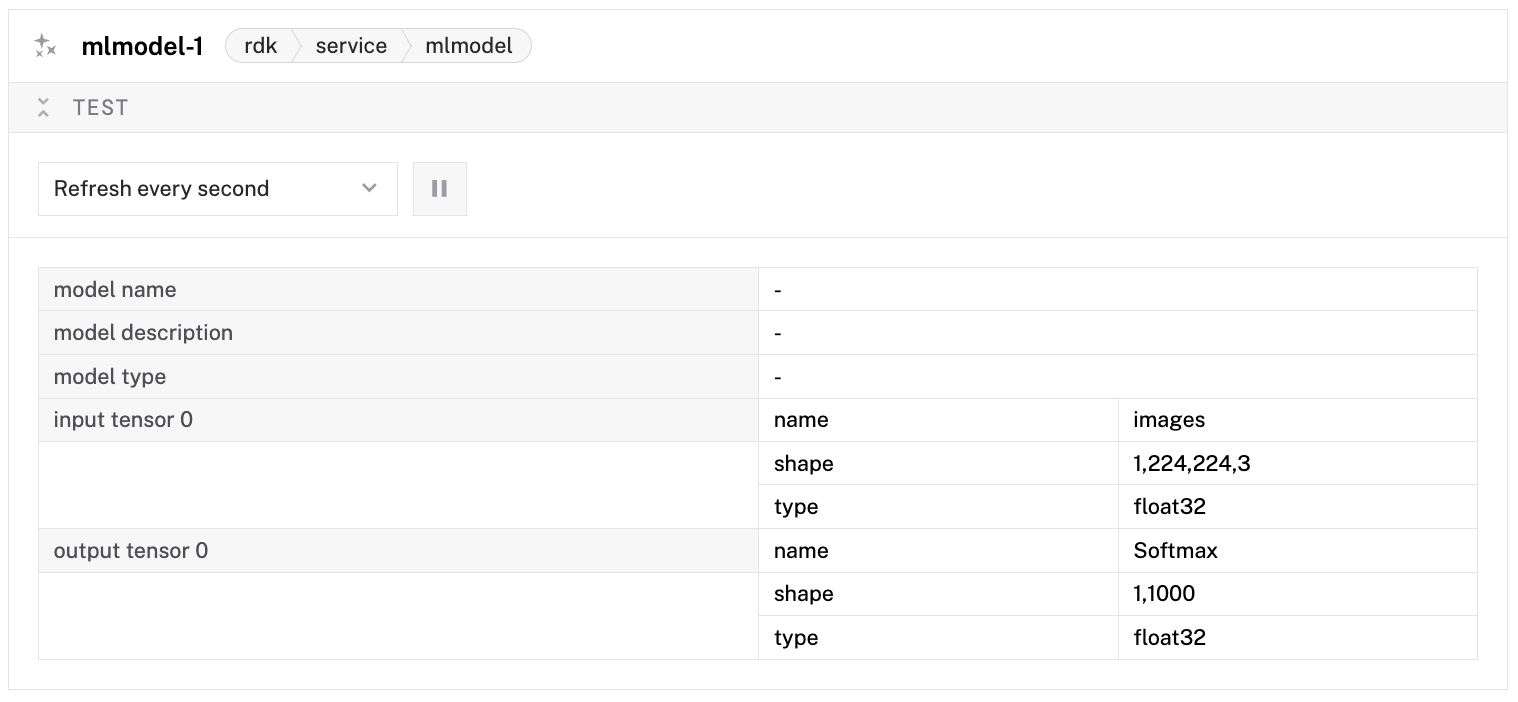
The following code passes an image to an ML model service, and uses the Infer method to make inferences:
import asyncio
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from viam.components.camera import Camera
from viam.media.utils.pil import viam_to_pil_image
from viam.robot.client import RobotClient
from viam.services.mlmodel import MLModelClient
# Configuration constants – replace with your actual values
API_KEY = "" # API key, find or create in your organization settings
API_KEY_ID = "" # API key ID, find or create in your organization settings
MACHINE_ADDRESS = "" # the address of the machine you want to capture images from
ML_MODEL_NAME = "" # the name of the ML model you want to use
CAMERA_NAME = "" # the name of the camera you want to capture images from
async def connect_machine() -> RobotClient:
"""Establish a connection to the robot using the robot address."""
machine_opts = RobotClient.Options.with_api_key(
api_key=API_KEY,
api_key_id=API_KEY_ID
)
return await RobotClient.at_address(MACHINE_ADDRESS, machine_opts)
async def main() -> int:
machine = await connect_machine()
camera = Camera.from_robot(machine, CAMERA_NAME)
ml_model = MLModelClient.from_robot(machine, ML_MODEL_NAME)
# Get ML model metadata to understand input requirements
metadata = await ml_model.metadata()
# Capture image
image_frame = await camera.get_image()
# Convert ViamImage to PIL Image first
pil_image = viam_to_pil_image(image_frame)
# Convert PIL Image to numpy array
image_array = np.array(pil_image)
# Get expected input shape from metadata
expected_shape = list(metadata.input_info[0].shape)
expected_dtype = metadata.input_info[0].data_type
expected_name = metadata.input_info[0].name
if not expected_shape:
print("No input info found for 'image'")
return 1
if len(expected_shape) == 4 and expected_shape[0] == 1 and expected_shape[3] == 3:
expected_height = expected_shape[1]
expected_width = expected_shape[2]
# Resize to expected dimensions
if image_array.shape[:2] != (expected_height, expected_width):
pil_image_resized = pil_image.resize((expected_width, expected_height))
image_array = np.array(pil_image_resized)
else:
print(f"Unexpected input shape format.")
return 1
# Add batch dimension and ensure correct shape
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_array, axis=0)
# Ensure the data type matches expected type
if expected_dtype == "uint8":
image_data = image_data.astype(np.uint8)
elif expected_dtype == "float32":
# Convert to float32 and normalize to [0, 1] range
image_data = image_data.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
else:
# Default to float32 with normalization
image_data = image_data.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
# Create the input tensors dictionary
input_tensors = {
expected_name: image_data
}
output_tensors = await ml_model.infer(input_tensors)
print(f"Output tensors:")
for key, value in output_tensors.items():
print(f"{key}: shape={value.shape}, dtype={value.dtype}")
await machine.close()
return 0
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
The following code passes an image to an ML model service, and uses the Infer method to make inferences:
package main
import (
"bytes"
"context"
"fmt"
"image"
"image/jpeg"
"gorgonia.org/tensor"
"go.viam.com/rdk/logging"
"go.viam.com/rdk/ml"
"go.viam.com/rdk/robot/client"
"go.viam.com/rdk/components/camera"
"go.viam.com/rdk/services/mlmodel"
"go.viam.com/rdk/utils"
"go.viam.com/utils/rpc"
)
func main() {
apiKey := ""
apiKeyID := ""
machineAddress := ""
mlModelName := ""
cameraName := ""
logger := logging.NewDebugLogger("client")
ctx := context.Background()
machine, err := client.New(
context.Background(),
machineAddress,
logger,
client.WithDialOptions(rpc.WithEntityCredentials(
apiKeyID,
rpc.Credentials{
Type: rpc.CredentialsTypeAPIKey,
Payload: apiKey,
})),
)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
// Capture image from camera
cam, err := camera.FromRobot(machine, cameraName)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
imageData, _, err := cam.Image(ctx, utils.MimeTypeJPEG, nil)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
// Decode the image data to get the actual image
img, err := jpeg.Decode(bytes.NewReader(imageData))
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
// Get ML model metadata to understand input requirements
mlModel, err := mlmodel.FromRobot(machine, mlModelName)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
metadata, err := mlModel.Metadata(ctx)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
// Get expected input shape and type from metadata
var expectedShape []int
var expectedDtype tensor.Dtype
var expectedName string
if len(metadata.Inputs) > 0 {
inputInfo := metadata.Inputs[0]
expectedShape = inputInfo.Shape
expectedName = inputInfo.Name
// Convert data type string to tensor.Dtype
switch inputInfo.DataType {
case "uint8":
expectedDtype = tensor.Uint8
case "float32":
expectedDtype = tensor.Float32
default:
expectedDtype = tensor.Float32 // Default to float32
}
} else {
logger.Fatal("No input info found in model metadata")
}
// Resize image to expected dimensions
bounds := img.Bounds()
width := bounds.Dx()
height := bounds.Dy()
// Extract expected dimensions
if len(expectedShape) != 4 || expectedShape[0] != 1 || expectedShape[3] != 3 {
logger.Fatal("Unexpected input shape format")
}
expectedHeight := expectedShape[1]
expectedWidth := expectedShape[2]
// Create a new image with the expected dimensions
resizedImg := image.NewRGBA(image.Rect(0, 0, expectedWidth, expectedHeight))
// Simple nearest neighbor resize
for y := 0; y < expectedHeight; y++ {
for x := 0; x < expectedWidth; x++ {
srcX := x * width / expectedWidth
srcY := y * height / expectedHeight
resizedImg.Set(x, y, img.At(srcX, srcY))
}
}
// Convert image to tensor data
tensorData := make([]float32, 1*expectedHeight*expectedWidth*3)
idx := 0
for y := 0; y < expectedHeight; y++ {
for x := 0; x < expectedWidth; x++ {
r, g, b, _ := resizedImg.At(x, y).RGBA()
// Convert from 16-bit to 8-bit and normalize to [0, 1] for float32
if expectedDtype == tensor.Float32 {
tensorData[idx] = float32(r>>8) / 255.0 // R
tensorData[idx+1] = float32(g>>8) / 255.0 // G
tensorData[idx+2] = float32(b>>8) / 255.0 // B
} else {
// For uint8, we need to create a uint8 slice
logger.Fatal("uint8 tensor creation not implemented in this example")
}
idx += 3
}
}
// Create input tensor
var inputTensor tensor.Tensor
if expectedDtype == tensor.Float32 {
inputTensor = tensor.New(
tensor.WithShape(1, expectedHeight, expectedWidth, 3),
tensor.WithBacking(tensorData),
tensor.Of(tensor.Float32),
)
} else {
logger.Fatal("Only float32 tensors are supported in this example")
}
// Convert tensor.Tensor to *tensor.Dense for ml.Tensors
denseTensor, ok := inputTensor.(*tensor.Dense)
if !ok {
logger.Fatal("Failed to convert inputTensor to *tensor.Dense")
}
inputTensors := ml.Tensors{
expectedName: denseTensor,
}
outputTensors, err := mlModel.Infer(ctx, inputTensors)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("Output tensors: %v\n", outputTensors)
err = machine.Close(ctx)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
}
There are a range of vision services that interpret images. Some vision services apply an ML model to a stream of images from a camera to:
To use a vision service:
Visit your machine’s CONFIGURE or CONTROL page.
Expand the TEST area of the vision service panel.
The feed shows an overlay of detected objects or classifications on top of a live camera feed.

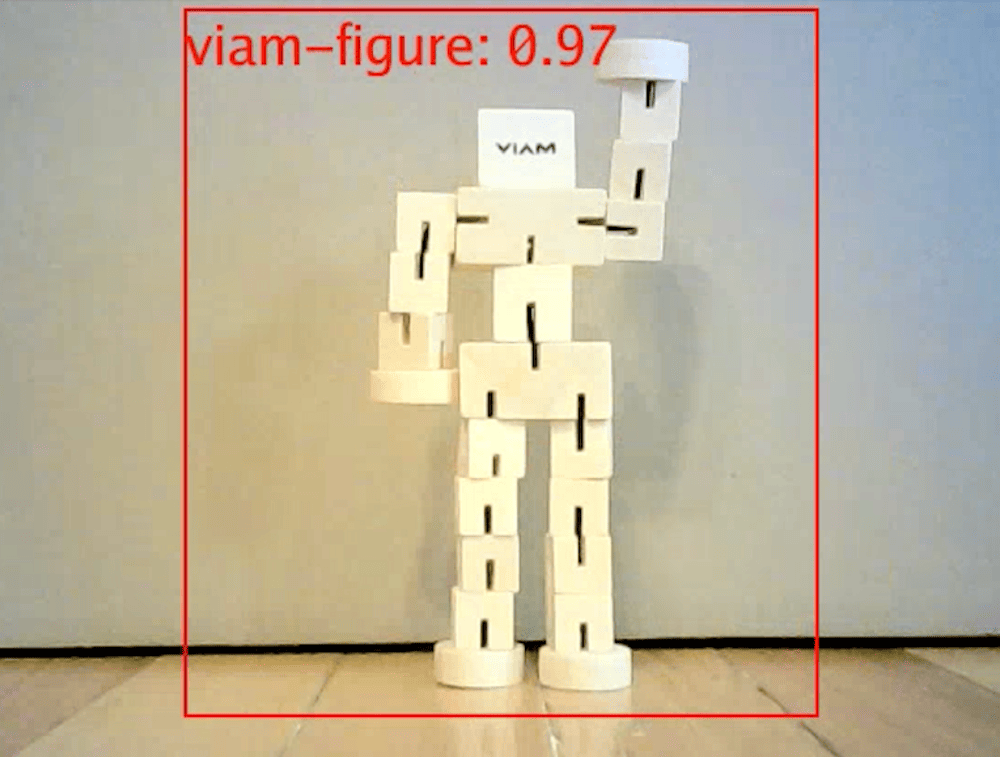
The following code passes an image from a camera to a vision service and uses the GetClassifications method:
import asyncio
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from viam.components.camera import Camera
from viam.media.utils.pil import viam_to_pil_image
from viam.robot.client import RobotClient
from viam.services.vision import VisionClient
# Configuration constants – replace with your actual values
API_KEY = "" # API key, find or create in your organization settings
API_KEY_ID = "" # API key ID, find or create in your organization settings
MACHINE_ADDRESS = "" # the address of the machine you want to capture images from
CLASSIFIER_NAME = "" # the name of the classifier you want to use
CAMERA_NAME = "" # the name of the camera you want to capture images from
async def connect_machine() -> RobotClient:
"""Establish a connection to the robot using the robot address."""
machine_opts = RobotClient.Options.with_api_key(
api_key=API_KEY,
api_key_id=API_KEY_ID
)
return await RobotClient.at_address(MACHINE_ADDRESS, machine_opts)
async def main() -> int:
machine = await connect_machine()
camera = Camera.from_robot(machine, CAMERA_NAME)
classifier = VisionClient.from_robot(machine, CLASSIFIER_NAME)
# Capture image
image_frame = await camera.get_image(mime_type="image/jpeg")
# Get tags using the ViamImage (not the PIL image)
tags = await classifier.get_classifications(
image=image_frame, image_format="image/jpeg", count=2)
await machine.close()
return 0
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
The following code passes an image from a camera to a vision service and uses the GetClassifications method:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"image/jpeg"
"bytes"
"go.viam.com/rdk/logging"
"go.viam.com/rdk/robot/client"
"go.viam.com/rdk/services/vision"
"go.viam.com/rdk/components/camera"
"go.viam.com/rdk/utils"
"go.viam.com/utils/rpc"
)
func main() {
apiKey := ""
apiKeyID := ""
machineAddress := ""
classifierName := ""
cameraName := ""
logger := logging.NewDebugLogger("client")
ctx := context.Background()
machine, err := client.New(
context.Background(),
machineAddress,
logger,
client.WithDialOptions(rpc.WithEntityCredentials(
apiKeyID,
rpc.Credentials{
Type: rpc.CredentialsTypeAPIKey,
Payload: apiKey,
})),
)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
// Capture image from camera
cam, err := camera.FromRobot(machine, cameraName)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
imageData, _, err := cam.Image(ctx, utils.MimeTypeJPEG, nil)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
// Convert binary data to image.Image
img, err := jpeg.Decode(bytes.NewReader(imageData))
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
// Get classifications using the image
classifier, err := vision.FromRobot(machine, classifierName)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
classifications, err := classifier.Classifications(ctx, img, 2, nil)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
err = machine.Close(ctx)
if err != nil {
logger.Fatal(err)
}
}
The following code passes an image from a camera to a vision service and uses the GetClassifications method:
import { createRobotClient, RobotClient, VisionClient, CameraClient } from "@viamrobotics/sdk";
// Configuration constants – replace with your actual values
let API_KEY = ""; // API key, find or create in your organization settings
let API_KEY_ID = ""; // API key ID, find or create in your organization settings
let MACHINE_ADDRESS = ""; // the address of the machine you want to capture images from
let CLASSIFIER_NAME = ""; // the name of the classifier you want to use
let CAMERA_NAME = ""; // the name of the camera you want to capture images from
async function connectMachine(): Promise<RobotClient> {
// Establish a connection to the robot using the machine address
return await createRobotClient({
host: MACHINE_ADDRESS,
credentials: {
type: 'api-key',
payload: API_KEY,
authEntity: API_KEY_ID,
},
signalingAddress: 'https://app.viam.com:443',
});
}
async function main(): Promise<number> {
const machine = await connectMachine();
const camera = new CameraClient(machine, CAMERA_NAME);
const classifier = new VisionClient(machine, CLASSIFIER_NAME);
// Capture image
const imageFrame = await camera.getImage();
// Get tags using the image
const tags = await classifier.getClassifications(
imageFrame,
imageFrame.width ?? 0,
imageFrame.height ?? 0,
imageFrame.mimeType ?? "",
2
);
return 0;
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error("Script failed:", error);
process.exit(1);
});
Cloud inference enables you to run machine learning models in the Viam cloud, instead of on a local machine. Cloud inference provides more computing power than edge devices, enabling you to run more computationally-intensive models or achieve faster inference times.
You can run cloud inference using any TensorFlow and TensorFlow Lite model in the Viam registry, including unlisted models owned by or shared with you.
To run cloud inference, you must pass the following:
You can obtain the binary data ID from the DATA tab and the organization ID by running the CLI command viam org list.
You can find the model information on the MODELS tab.
viam infer --binary-data-id <binary-data-id> --model-name <model-name> --model-org-id <org-id-that-owns-model> --model-version "2025-04-14T16-38-25" --org-id <org-id-that-executes-inference>
Inference Response:
Output Tensors:
Tensor Name: num_detections
Shape: [1]
Values: [1.0000]
Tensor Name: classes
Shape: [32 1]
Values: [...]
Tensor Name: boxes
Shape: [32 1 4]
Values: [...]
Tensor Name: confidence
Shape: [32 1]
Values: [...]
Annotations:
Bounding Box Format: [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max]
No annotations.
The command returns a list of detected classes or bounding boxes depending on the output of the ML model you specified, as well as a list of confidence values for those classes or boxes.
The bounding box output uses proportional coordinates between 0 and 1, with the origin (0, 0) in the top left of the image and (1, 1) in the bottom right.
For more information, see viam infer.
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! If you have any other feedback please let us know:
We're sorry about that. To help us improve, please tell us what we can do better:
Thank you!